Persia
-
Persia is ancient name of
modern
Iran.
The country was known by this name before the conquests of Alexander the
Great and after the fall of the Arab
empire. The original Persian empire which was built by the
Achaemenid dynasty and fell to Alexander the Great. was based east of the Persian Gulf, but at its
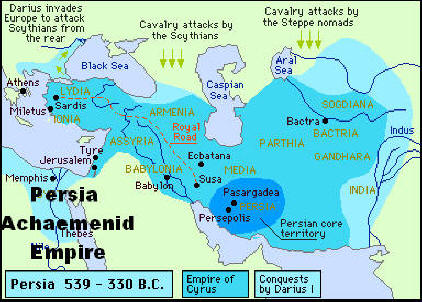
height it extended westward to the Mediterranean sea, under Cyrus and
Darius, as shown in the map below. Susa was the capital city of ancient
Persia, and Persepolis was a major city.
Ancient Persia was a mixture of
cultures and ethnicities. As has been pointed out,1 Persia, like ancient
Rome, built its culture on the cultures of its subjugated peoples, including
the Assyrians and Babylonians.
The history of Persia is divided into several periods:
The
Achaemenid dynasty united Persia, challenged ancient Greece and
destroyed the ancient Babylonian and Assyrian empires. The
Achaemenid dynasty came to an end with the conquests of Alexander the
Great.
From about 330 BCE, the
Arsacid dynasty ruled
Parthia,
which came to be almost as great as ancient Persia.
The
Sassanid dynasty replaced the
Arsacid dynasty about 330 and challenged Rome. The
Sassanid dynasty made
Zoroastrianism the state religion.
It was ended in 651 by the Arab
conquest and the rise of
Islam.
After the breakup of the Arab
empire, Persia was ruled by a number of dynasties, which usually were begun by
provincial governors under the Arab
Caliphs.
Two of the most important of these were the
Samanid and
Ghaznavid dynasties. The reigned over a large and changing territory
comprising eastern
Persia,
modern Afghanistan what is now referred to as central Asia and a part of
modern Pakistan. The
Samanids were apparently originally Afghani, and the
Ghaznavid rulers were Turkic people, originally slaves employed as soldiers.
Both dynasties furthered the
Persian
language and culture to differentiates themselves and isolate their empires from
Turkish and Arab
influences.
After the invasions of the Mongols, Persia was reunited by the
Safavid
dynasty which arose about 1501. The
Safavids made
Shia
Islam
the state religion of Persia. The long
Safavid
rule ended about 1746 in civil war. Most of Persia was then ruled by the
Zand
dynasty, but the northeastern region was ruled by the Afsharid
khans,
The
Qajar
dynasty reunited Persia in 1796, but
Qajar
Persia was weak and debt ridden. A constitution was promulgated in 1911, but
remained largely decorative. The
Qajar
dynasty was overthrown in 1929 by Reza Shah, founder of the
Pahlavi dynasty, who renamed the country
Iran.
References
1. 1. Madadi, Ben,
Not that Special, Iranian, Nov. 14, 2006,
http://www.iranian.com/Madadi/2006/November/Persians110/index.html
Ami Isseroff
October 11, 2010
Synonyms and alternate spellings:
Iran, Parthia
Further Information:
A Brief
History of modern Iran Map of
Iran, Ahmadinejad,
Mahmoud,
Khomeini, Ayatollah Ruholla Parthia,
|